Sentence Structure in English Grammar: Types, Rules, Examples, and Practice Exercises
Select Your Practice Test- Choose Your Difficult Level
Easy – Class 6 & Class 7 – Intermediate – Class 7 & Class 8 & Class 9 – HARD – Class 10 , CLASS 11- 12
MCQ Test, Self Assessment
| Chapter | Test Type |
|---|---|
| Easy | |
| Intermediate | |
| Hard |
What is Sentence Structure?
Sentence structure refers to the way words, phrases, and clauses are arranged to form a meaningful sentence. It involves understanding how subjects, verbs, objects, and modifiers come together to convey complete ideas.
✨ Why is Sentence Structure Important?
- 📘 Clarity: Ensures your message is clear.
- 🧠 Logic: Helps you express cause-effect, conditions, comparisons, etc.
- 📚 Grammar: Supports correct use of tense, voice, and punctuation.
- ✍️ Writing Style: Makes your writing more engaging and dynamic.
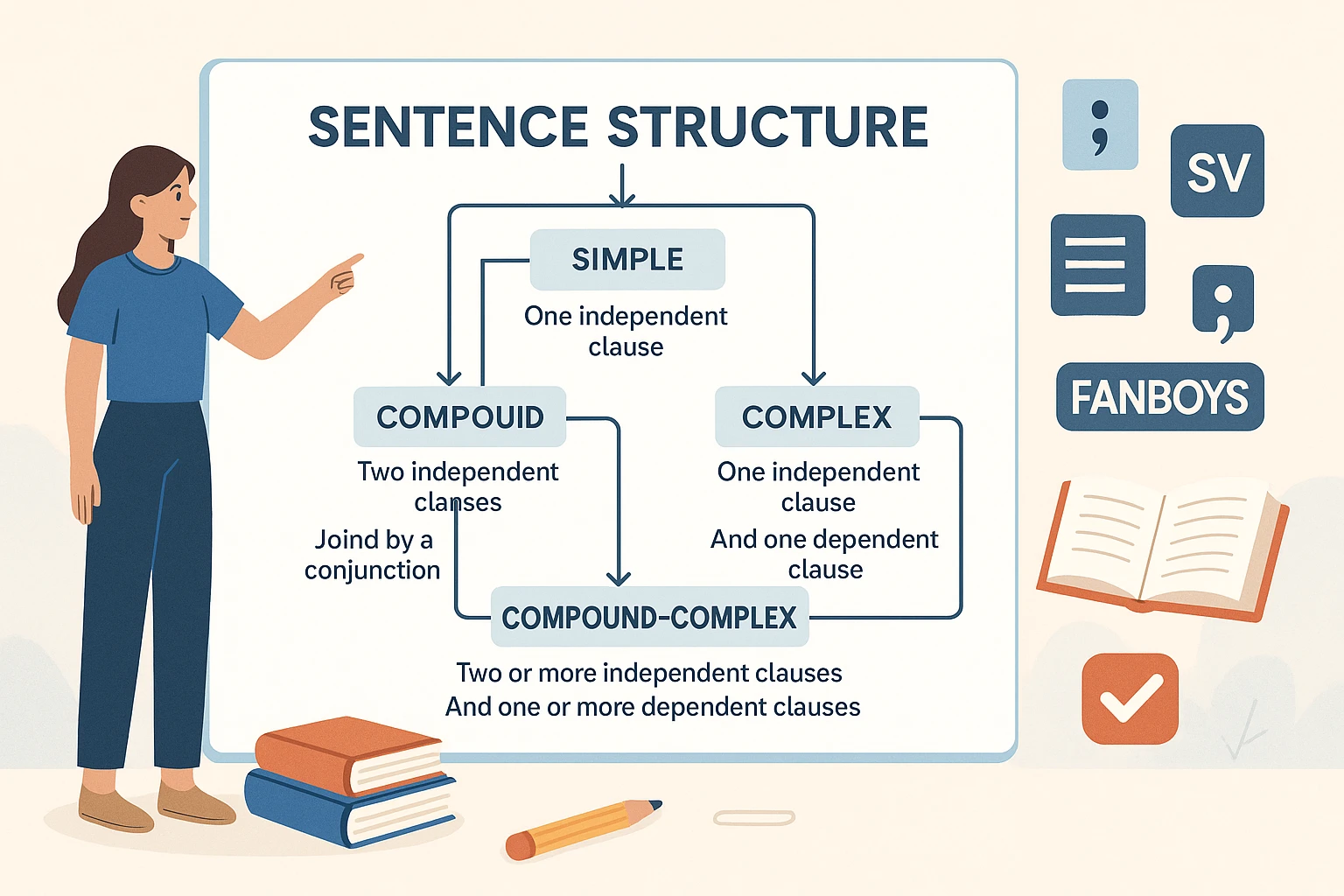
📊 Types of Sentence Structures
| Type of Sentence | Structure Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | She studies. | One independent clause |
| Compound | She studies and he plays. | Two independent clauses joined by a conjunction |
| Complex | She studies because she cares. | One independent + one dependent clause |
| Compound-Complex | She studies because she cares, and he plays. | Two independent + one/more dependent clauses |
🔍 Parts of a Sentence
| Part | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Subject | Who or what the sentence is about | The cat slept. |
| Predicate | The action or state of the subject | The cat slept. |
| Object | The receiver of the action | She read a book. |
| Clause | Group of words with subject + verb | She left because it rained. |
| Phrase | Group of words without full clause | In the morning, very fast |
🧩 Sentence Structure Rules
- ✅ Every sentence must have a subject and verb.
- ✅ Simple sentences can have compound subjects or verbs.
- She sings and dances.
- ✅ Compound sentences must use coordinating conjunctions (FANBOYS).
- for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
- ✅ Complex sentences require subordinating conjunctions:
- because, although, since, if, when, unless
- ✅ Use punctuation properly to avoid run-on or fragmented sentences.
📘 Common Sentence Errors and Fixes
| Error Type | Example | Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Fragment | Because she was late. | She was late, so she missed it. |
| Run-on | I went he stayed. | I went, but he stayed. |
| Comma splice | She came, she saw. | She came; she saw. / She came and saw. |
| Subject-verb error | They goes to school. | They go to school. |
🌐 Comparison of Sentence Types
| Feature | Simple | Compound | Complex | Compound-Complex |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Clause | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 2+ |
| Dependent Clause | 0 | 0 | 1+ | 1+ |
| Uses Conjunctions? | No | Yes (FANBOYS) | Yes (Subordinators) | Both types |
| Example | She eats. | She eats and he drinks. | She eats because she’s hungry. | She eats because she’s hungry, and he drinks. |
💡 Tips & Tricks for Better Sentence Formation
🔹 Use varied sentence types in writing to make it more interesting.
🔹 Start with simple structure, then expand into complex types.
🔹 Avoid long, confusing run-ons—use punctuation and conjunctions.
🔹 Read aloud to check if a sentence sounds complete.
🔹 Practice clause joining with common conjunctions.
🛠️ Quick Chart: Coordinating & Subordinating Conjunctions
| Coordinating (FANBOYS) | Subordinating |
|---|---|
| For | Because, although, since |
| And | If, unless, until |
| Nor | When, while, whenever |
| But | Though, even though |
| Or | After, before, once |
| Yet | As, as if, as though |
| So | Whereas, provided that |
🧪 Practice Section (With Mixed Types)
1. Identify the sentence type:
“Although he was tired, he continued working.”
→ Complex Sentence
2. Spot the error:
“They enjoys playing chess and reading.”
→ Error: enjoys → enjoy
3. Combine using a compound sentence:
“She studied hard. She passed the test.”
→ She studied hard, and she passed the test.
4. Transform into complex sentence:
“He missed the bus. He woke up late.”
→ He missed the bus because he woke up late.